Professor
Degrees and Appointments
- B.S. 1962, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Sc.D. 1966, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Field of Study: Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry
Research Specialties: Chemical Physics, Energy Science, Instrument Development, Spectroscopy/Molecular Structure, Synthesis/Synthetic Methods Development, Theory, Modeling, and Simulation, Foundational Molecular Science
Research
STRUCTURES OF MOLECULES FROM MICROWAVE SPECTROSCOPY
Microwave spectroscopy can provide detailed and accurate 3-D structures for many small molecules. These structures usually provide coordinates with accuracies of 0.01Å for the free molecules in the gas phase. The gas phase structures can be directly compared with high-level theoretical calculations. For many cases additional splittings in the high-resolution spectra give information on quadrupole coupling and other interactions which provide details on the electronic charge distribution (where the electrons are) in the molecules. Pulsed-beam, Fourier-transform spectrometers provide the required sensitivity and resolution to make these measurements on a wide variety of molecules. The extremely high sensitivity and high resolution of the pulsed-beam, Fourier transform microwave spectrometer (Flygare-Balle spectrometer) systems have opened the door for numerous new structural measurements on larger and less stable molecules and complexes. One of these Flygare-Balle spectrometers has been working in our lab for 27 years and a new, much larger one has been in operation since 2010.
TRANSITION METAL COMPLEXES
Many of our recent measurements have been focused on transition metal complexes, since this class of compounds plays so many important roles in the chemical industry and in biological systems. Transition metal complexes play many important roles in the chemical industry, in biological systems and as an area of study in inorganic chemistry. Millions of tons of chemical products are produced each year using reactions with transition metal catalysts. The active sites of many enzymes and transport proteins in living systems involve transition metal complexes. Due to the great importance of these systems, a large fraction of the research and study in inorganic chemistry is focused on transition metal complexes. Most of the published microwave structures of this important class of molecules have come from this work at the University of Arizona. Only a few examples had been reported earlier, using lower-resolution microwave methods.
HYDROGEN-BONDED COMPLEXES
Many recent measurements have been made on hydrogen-bonded complexes. Hydrogen bonding is important in many areas of chemistry and biochemistry. We have done detailed measurements of hydrogen bonding, focusing on complexes with 2 hydrogen bonds and proton tunneling.
RECENT RESEARCH RESULTS
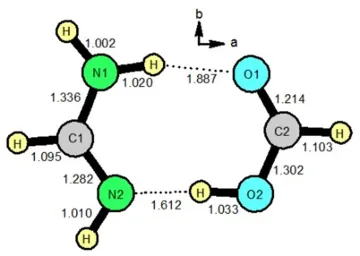
1) Synthesis, microwave spectra, x-ray structure and high-level theoretical calculations for formamidinium formate The microwave spectrum, x-ray structure and high-level theoretical calculations were reported for formamidinium formate, the doubly hydrogen bonded dimer between formamidine and formic acid. This is the first microwave study of a doubly hydrogen bonded structure with two N-H hydrogen bonds. Calculated rotational constants are in very good agreement with the measured values, supporting the doubly bonded structure. However, the calculated quadrupole coupling parameters do not agree well with the measured values. We interpret this as strong evidence for large amplitude vibrational motions of the protons involved in the hydrogen bonding.
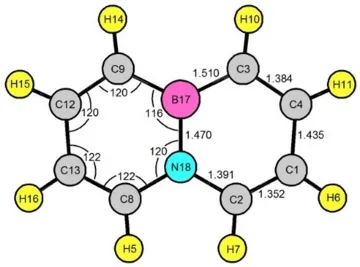
2) Microwave Spectra, Molecular Structure and Aromatic Character of 4a,8a- Azaboranaphthalene (B-N naphthalene) The microwave spectra for seven unique isotopologues of BN-naphthalene were measured using a pulsed-beam Fourier transform microwave spectrometer. Spectra were obtained for the normal isotopologues with 10B, 11B, and all unique single 13C and the 15N isotopologue (with 11B), IN NATURAL ABUNDANCE. This is very likely the largest molecule for which 15N isotopologue spectra have been measured in natural abundance with a pulsed-beam F-T spectrometer.
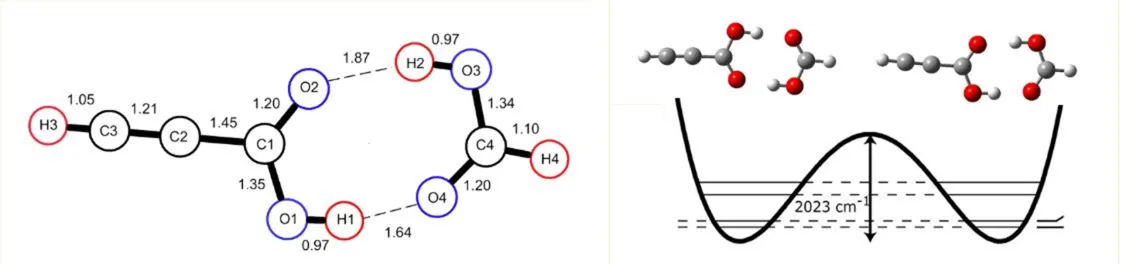
3) Proton Tunneling In the Formic Acid - Propiolic Acid Dimer Hydrogen bonds are often not simply static structural features, but can display interesting and complex dynamic effects. The propiolic acid- formic acid (Pro-FA) dimer has a symmetric double well potential and exhibits observable concerted proton tunneling. The tunneling frequencies were directly determined by observing both the a-type and b-type transitions in the dimers. We reported preliminary microwave measurements of concerted proton tunneling splittings for the formic acid – propiolic acid dimer in 2010. A much larger set of measurements covering 1-22 GHz, including collaboration with the Pate group at the University of Virginia was been published in 2011. All of the observed transitions were split into doublets by the effects of the concerted tunneling of the two acid protons. An analysis of the data on all measured isotopomers reveals that the complex is planar and the monomer centers of mass are separated by 3.87(2) Å. The “best fit” concerted proton tunneling splitting is 290 MHz.
4) The large cavity spectrometer provides the highest resolution available (2 kHz) for pulsed-beam Fourier transform microwave spectrometers and allows us to observe and accurately measure the small splittings caused by deuterium eQq terms. The deuterium quadrupole coupling constants may be very useful in sorting out different conformations of larger molecules in future work. Measured coupling constants are in the range eQq(D) = 0.166 to 0.284 MHz.

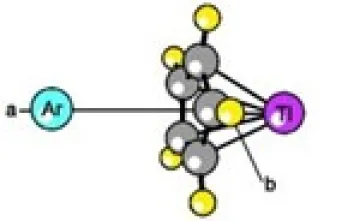
B) ARGON-CYCLOPENTADIENYL THALLIUM - WEAKLY-BOUND COMPLEX
This is the FIRST report of microwave measurements on a weakly-bound complex formed between a noble gas and an organometallic molecule. Accurate structures were obtained from the measurements and MP2 calculations on this complex. Calculations and microwave searches for other weakly-bound complexes with small organic molecules were done but this is the first to be successful. The argon atom is located on the a-axis of the C5H5Tl monomer, directly opposite from the thallium metal atom. The measured separation distance between argon and the cyclopentadienyl ring is R = 3.56Å. The experimental binding energy is E = 339 cm-1.
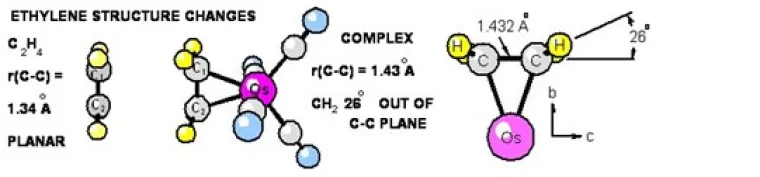
C) SPECTRA AND STRUCTURE FOR ETHYLENE OSMIUM TETRACARBONYL
Changes in the structure of ethylene on coordination to Os(CO)4 were accurately measured and reported recently. Rotational spectra of seven isotopomers of tetracarbonylethyleneosmium, Os(CO)4(C2H4), were measured in the 4 -12 GHz. Olefin-transition metal complexes of this type occur extensively in recent organic syntheses and serve as important models for transition states in the metal-mediated transformations of alkenes. Using experimental rotational constants a near-complete gas-phase r0 structure was determined. The changes in the structure of ethylene on coordination are large and well-determined. For the complex the experimental ethylene C-C bond length is 1.432(5)Å, which falls between the free ethylene value of 1.3391(13)Å and the ethane value of 1.534(2)Å. The angle between the plane of the CH2 group and the extended ethylene C-C bond (angle out-of-plane) is 26.0(3)°, indicating that this complex is better described as a metallacyclopropane than a Π bonded olefin-metal complex. The Os-C-C-H dihedral angle is 107.4(1)Å, indicating that the ethylene carbon atoms have near sp3 character in the complex.
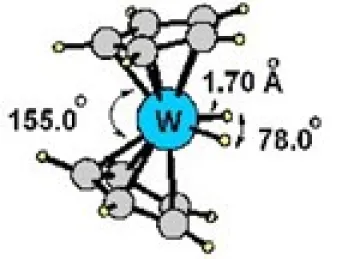
D) BIS(η5-CYCLOPENTADIENYL)TUNGSTEN DIHYDRIDE
To the best of our knowledge, this work marks the first microwave study of a bent metallocene complex. Microwave spectra for 11 isotopomers of bis(η5-cyclopentadienyl)tungsten dihydride ((C5H5)2WH2) were recorded in the 5-14 GHz region and used to obtain a nearly complete 3D structure for this complex. The hydrogen atom separation is r(H-H) = 2.14(1)Å, indicating that this is clearly a "classical dihydride" rather than an η2dihydrogen" complex.
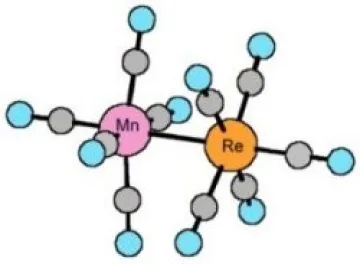
E) FIRST MICROWAVE SPECTRUM OF A DINUCLEAR COMPLEX
Rotational constants for the 187Re and 185Re isotopomers of this complex are 200.369, and 200.556 MHz, which makes it one of the complexes with highest moment of inertia(i.e. largest molecules) studied by microwave spectroscopy. This symmetric-top complex exhibits a very complicated spectrum due to large quadrupole coupling interactions for both 185Re and 187Re isotopes and for Mn. This work appears to be the first microwave measurements of the rotational spectrum of a transition metal - dinuclear complex. Metal-metal bonding interactions have continued to be an important area in inorganic chemistry. Some of the most effective catalysts for chiral syntheses have been dirhodium transition metal complexes.
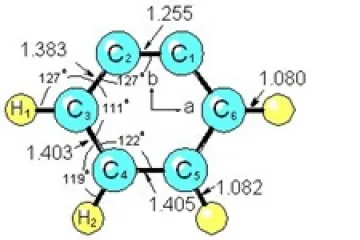
F) ACCURATE STRUCTURE FOR O-BENZYNE
A complete, highly accurate and precise near-equilibrium structure for the radical o-benzyne has been obtained by measuring rotational spectra for 7 isotopomers, and including calculated vibrational averaging corrections in the analysis. This is the first structure determination for this radical. The key to obtaining the accurate, near-equilibrium structure for o-benzyne was the inclusion of accurate, calculated vibration-rotation interaction constants in the least squares fit analysis to obtain the structural parameters.
Microwave measurements of the complete three-dimensional structures were made for six transition metal hydrides. There has been much recent interest in examining transition metal complexes with two or more H atoms following the National interest in storing HYDROGEN as an automotive fuel.
During the course of our research, graduate students receive training and experience in a number of different techniques and areas. They would obtain "hands-on" experience in at least a few of the following areas: computer interfacing, programing for data analyis and/or and DFT calculations, apparatus development and construction, electronic, microwave and vacuum systems, molecular spectroscopy, molecular structures and inorganic synthesis.
“Measurements of Microwave and NMR Spectra for 15N Substituted Formamidinium Formate,” Zunwu Zhou, Coralyse Peureux, R. Alan Aitken, and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Mol. Spectrosc. 378, 111478 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jms.2021.111478
“Microwave spectra and theoretical calculations for two structural isomers of methylmanganese pentacarbonyl,” Chakree Tanjaroon, Zunwu Zhou, David Mills, Kristen Keck, and Stephen G. Kukolich, Inorganic Chemistry 59, 9, 6432–6438, April 22, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00524
“Synthesis, microwave spectra, x-ray structure and high-level theoretical calculations for formamidinium formate,” Zunwu Zhou, R. Alan Aitken, Charlotte Cardinaud, Alexandra M. Z. Slawin, Honghao Wang, Adam M. Daly, Michael H. Palmer and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Chem. Phys. 150, 094305 (2019); (published online, 06 March 2019), https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5081683
“Rotational spectrum and structure of the T-shaped cyanoacetylene carbon dioxide complex, HCCCN···CO2,” L. Kang, P. Davis, I. Dorell, K. Li, O. Oncer, L. Wang, S. E. Novick, S. G. Kukolich, J. Mol. Spectrosc. 342, 62-72 (2017), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jms.2017.07.001
“Microwave Spectra, Molecular Structure and Aromatic Character of 4a,8a-Azaboranaphthalene," Aaron M. Pejlovas, Adam M. Daly, Arthur J. Ashe, III and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Chem. Phys. 144, 114303 (2016), http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4943882
“Microwave Measurements of the Tropolone – Formic Acid Doubly Hydrogen Bonded Dimer,” Aaron M. Pejlovas, Agapito Serrato III, Wei Lin, Stephen G. Kukolich, J Chem Phys 144(4), 044306/1-044306/3. (2016) http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4940775
“Microwave measurements of the rotational spectrum and gas phase structural parameters of the maleimide – formic acid dimer,” Aaron M. Pejlovas and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Mol. Spectrosc. 321, 1-4 (2016) http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jms.2016.01.011
"Microwave Spectra and Structure for the Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid-Formic Acid dimer," A. M. Pejlovas, W. Lin, and S. G. Kukolich, J. Chem. Phys. 143(12), 124311/1-124311/6. (2015) http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4931923
“Microwave measurements of proton tunneling and structural parameters for the propiolic acid – formic acid dimer,” Adam M. Daly, Kevin O. Douglass, Laszlo C. Sarkozy, Justin L. Neill, Matt T. Muckle, Daniel P. Zaleski, Brooks H. Pate and Stephen G. Kukolich, J Chem. Phys., 135(15), DOI: 154304/1-154304/12 (2011)
“Design, Construction and Testing of a Large-Cavity, 1-10 GHz Flygare-Balle Spectrometer,” Stephen G. Kukolich and Laszlo C. Sarkozy, Rev. Sci, Instrum., 82(9), DOI: 094103/1-094103/14. (2011)
"The rotational spectrum and structure for the argon-cyclopentadienyl thallium van der Waals complex: Experimental and computational studies of noncovalent bonding in an organometallic π-complex," Chakree Tanjaroon, Adam M. Daly, and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Chem. Phys. 129(5), 054305/1-054305/8 (2008)
"The Structure of Tetracarbonylethyleneosmium: Ethylene Structure Changes upon Complex Formation," Chandana Karunatilaka, Brandon S. Tackett, John Washington, and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(34), 10522-10530 (2007) (doi: 10.1021/ja0727969 S0002-7863(07)02796-5)
"Microwave Spectra and Gas-Phase Structural Parameters of Bis(η5Cyclopentadienyl)Tungsten Dihydride," Brandon S. Tackett, Chandana Karunatilaka, Adam Daly and Stephen G. Kukolich, Organometallics 26(8), 2070-2076 (2007)
"Equilibrium structure of gas phase o-benzyne," Peter Groner and Stephen G. Kukolich, J. Mol. Struc.780-781, 178-181 (2006) (doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2005.06.054)
"The rotational spectrum and theoretical study of a dinuclear complex, MnRe(CO)10," Chakree Tanjaroon, Kristen S. Keck, Stephen G. Kukolich, Michael H. Palmer, and Martyn F. Guest, J. Chem. Phys. 120, 4715-4725 (2004)
"Microwave Spectra, DFT Calculations and Molecular Structure of Acetylenemethyldioxorhenium," S. G. Kukolich, B. J. Drouin, O. Indris, J. J. Dannemiller, J. P. Zoller and W. A. Herrmann, J. Chem. Phys. 113, 7891-7900 (2000)
"Microwave Spectra and the Molecular Structure of Tetracarbonylethylene-iron," B. J. Drouin and S. G. Kukolich, J. Am. Chem Soc. 121, 4023-4030 (1999)
"Molecular Structure of Tetracarbonyldihydroiron: Microwave Measurements and Density Functional Theory Calculations," B. J. Drouin and S. G. Kukolich, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 6774-6780 (1998)






